Instructional coaching, a form of professional development for teachers, has become a cornerstone of educational improvement initiatives in recent years. It is a collaborative, ongoing process that aims to improve teaching and learning by providing teachers with personalized support in implementing effective teaching strategies. This article delves into the pedagogical knowledge that underpins instructional coaching, exploring its various aspects and their implications for teaching and learning.
Understanding pedagogical knowledge is crucial for instructional coaches as it forms the foundation of their work. It involves knowing how to teach, including understanding instructional strategies, learning theories, classroom management techniques, and assessment methods. This article provides a comprehensive glossary of key terms and concepts related to pedagogical knowledge in the context of instructional coaching.
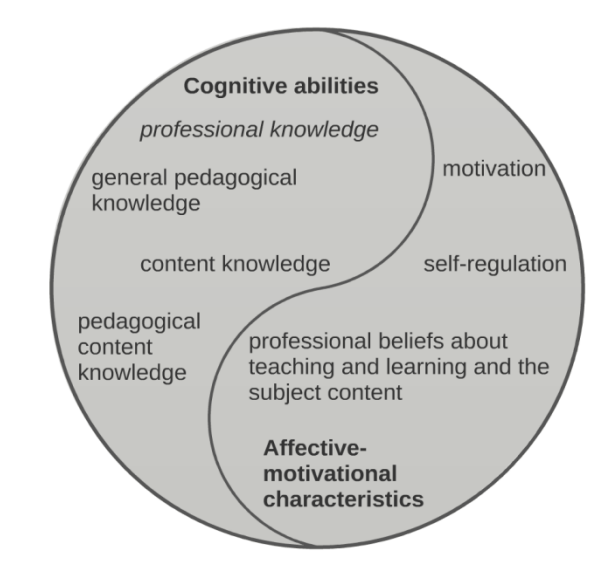
Concept of Pedagogical Knowledge
Pedagogical knowledge refers to the understanding and application of teaching methods and strategies that facilitate learning. It involves knowledge about how students learn, the nature of the curriculum, and the integration of technology in teaching and learning. Pedagogical knowledge is a critical component of a teacher’s professional competence, influencing their instructional decisions and actions in the classroom.
For instructional coaches, pedagogical knowledge is not just about knowing various teaching methods; it’s about understanding how these methods can be effectively implemented in different contexts. It’s about helping teachers to apply this knowledge in their classrooms, tailoring strategies to meet the unique needs of their students.
Components of Pedagogical Knowledge
Pedagogical knowledge comprises several key components, including knowledge of learning theories, instructional strategies, classroom management techniques, and assessment methods. Understanding these components allows instructional coaches to provide targeted support to teachers, helping them to enhance their teaching practice.
Learning theories, for example, provide insights into how students acquire knowledge and skills. Instructional strategies refer to the methods used to deliver content and facilitate learning, while classroom management techniques involve strategies for creating a positive learning environment. Assessment methods, on the other hand, are used to measure student learning and inform instruction.
Importance of Pedagogical Knowledge
Pedagogical knowledge is crucial for effective teaching. It enables teachers to make informed decisions about what teaching methods to use, how to structure their lessons, and how to manage their classrooms. Without a solid understanding of pedagogy, teachers may struggle to engage students in learning, leading to lower academic achievement.
For instructional coaches, pedagogical knowledge is equally important. It forms the basis of their work, enabling them to provide teachers with the support they need to improve their practice. By understanding pedagogy, coaches can help teachers to implement effective teaching strategies, manage their classrooms effectively, and use assessment data to inform their instruction.
Role of Instructional Coaching
Instructional coaching is a form of professional development that provides teachers with personalized, ongoing support in implementing effective teaching strategies. It is a collaborative process that involves working closely with teachers to enhance their teaching practice, with the ultimate goal of improving student learning.
Instructional coaches play a critical role in supporting teachers’ professional growth. They help teachers to reflect on their practice, identify areas for improvement, and implement new strategies. They also provide feedback and encouragement, helping teachers to build confidence in their abilities.
Coaching Strategies
Instructional coaches use a variety of strategies to support teachers, including modeling, observation, feedback, and collaborative planning. Modeling involves demonstrating effective teaching strategies, while observation allows coaches to assess teachers’ implementation of these strategies. Feedback provides teachers with constructive criticism and suggestions for improvement, and collaborative planning involves working together to develop lesson plans and instructional materials.
These strategies are not used in isolation; rather, they are integrated into a comprehensive approach to coaching. This approach is tailored to the needs of each teacher, taking into account their individual strengths, weaknesses, and goals.
Impact of Instructional Coaching
Research has shown that instructional coaching can have a significant impact on teaching and learning. It can lead to improvements in teachers’ instructional practices, increased student engagement, and higher student achievement. Moreover, it can foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement among teachers, promoting professional growth and collaboration.
However, the effectiveness of instructional coaching depends on several factors, including the quality of the coaching, the receptiveness of the teachers, and the support of the school leadership. Therefore, it is important for schools to invest in high-quality coaching programs and to create a supportive environment for coaching to thrive.
Integration of Pedagogical Knowledge in Instructional Coaching
Integrating pedagogical knowledge into instructional coaching involves helping teachers to apply their understanding of teaching methods in their classrooms. It involves working with teachers to develop effective lesson plans, implement engaging instructional strategies, manage their classrooms effectively, and use assessment data to inform their instruction.
Instructional coaches play a key role in this process. They provide teachers with the support they need to translate their pedagogical knowledge into practice, helping them to enhance their teaching skills and improve student learning.
Coaching for Pedagogical Knowledge
Coaching for pedagogical knowledge involves providing teachers with targeted support in areas such as learning theories, instructional strategies, classroom management, and assessment. This might involve helping teachers to understand how students learn, demonstrating effective teaching methods, providing feedback on classroom management techniques, or assisting with the analysis of assessment data.
The goal of this type of coaching is to enhance teachers’ pedagogical knowledge and skills, enabling them to implement effective teaching strategies and improve student learning. It requires a deep understanding of pedagogy, as well as the ability to provide constructive feedback and support.
Coaching for Pedagogical Application
Coaching for pedagogical application involves helping teachers to apply their pedagogical knowledge in their classrooms. This might involve assisting with lesson planning, modeling effective teaching strategies, observing teachers’ instruction and providing feedback, or collaborating on the development of instructional materials.
The goal of this type of coaching is to help teachers to translate their pedagogical knowledge into practice, enhancing their teaching skills and improving student learning. It requires a deep understanding of pedagogy, as well as the ability to provide practical, actionable support.
Challenges in Instructional Coaching
While instructional coaching can be highly effective, it is not without its challenges. These can include resistance from teachers, lack of support from school leadership, and limited resources. Understanding these challenges is crucial for instructional coaches, as it allows them to develop strategies to overcome them and maximize the impact of their coaching.
Resistance from teachers can stem from a variety of factors, including fear of criticism, lack of trust in the coach, or discomfort with change. To overcome this resistance, coaches need to build strong relationships with teachers, establish trust, and provide supportive, non-judgmental feedback.
Overcoming Resistance
Overcoming resistance in instructional coaching involves building strong relationships with teachers, establishing trust, and providing supportive, non-judgmental feedback. It requires patience, empathy, and excellent communication skills. Coaches need to listen to teachers’ concerns, understand their perspectives, and provide reassurance and encouragement.
Building trust is crucial in this process. Teachers need to feel confident that the coach is there to support them, not to criticize or judge them. This trust can be built through consistent, positive interactions, as well as through demonstrating competence and reliability.
Support from School Leadership
Support from school leadership is crucial for the success of instructional coaching. School leaders play a key role in creating a supportive environment for coaching, providing resources, and promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Without this support, coaches may struggle to make a significant impact.
School leaders can support instructional coaching in several ways. They can provide resources for coaching, such as time for coaches and teachers to meet, professional development opportunities for coaches, and materials and technology for coaching activities. They can also promote a culture of learning and improvement, emphasizing the value of coaching and encouraging teachers to engage in the coaching process.
Conclusion
Instructional coaching, underpinned by pedagogical knowledge, is a powerful tool for enhancing teaching and learning. It provides teachers with personalized, ongoing support in implementing effective teaching strategies, helping them to improve their practice and boost student achievement.
However, the success of instructional coaching depends on several factors, including the quality of the coaching, the receptiveness of the teachers, and the support of the school leadership. Therefore, it is crucial for schools to invest in high-quality coaching programs and to create a supportive environment for coaching to thrive.