What is PBIS in education? PBIS stands for Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports. It is a proactive approach used in schools to promote positive behavior and improve the overall learning environment. By focusing on teaching and reinforcing good behavior, PBIS aims to reduce disciplinary issues and help students succeed academically and emotionally.
Quick Insights Into PBIS
- PBIS is a framework focused on promoting positive behavior through proactive teaching and prevention strategies, moving away from traditional punitive disciplinary actions.
- The PBIS model operates on three tiers of support, providing universal, targeted, and intensive interventions to meet diverse student needs and improve behavioral outcomes.
- Successful PBIS implementation relies on data-driven decision making, consistent engagement across the school community, and ongoing monitoring and refinement of strategies.

Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a structured framework aimed at enhancing students’ behavioral, academic, and emotional well-being through evidence-based practices. The primary goal of PBIS is to create a positive school climate conducive to student learning and growth. Unlike traditional disciplinary methods that focus solely on punishing misbehavior, PBIS emphasizes teaching positive behavior interventions and appropriate behaviors.
The PBIS framework is both proactive and reactive, addressing behavior issues through prevention and instruction. It supports behavior in the context of a district’s Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS), integrating seamlessly with other school initiatives to form a comprehensive model of behavior. Focusing on increasing positive behaviors and preventing unwanted behaviors, PBIS aims to improve student outcomes and enhance school climate and culture.
In essence, PBIS represents a paradigm shift in behavior management, where the emphasis is on building a supportive environment that fosters positive behavior rather than merely responding to negative behavior. This approach not only helps in managing student behavior but also contributes to a more cohesive and productive learning environment.
The Core Principles of PBIS
At the heart of PBIS are its core principles, which guide the implementation of positive behavioral interventions across schools. These principles emphasize proactive strategies for defining, teaching, and supporting appropriate student behaviors. PBIS prioritizes teaching over punishment, operating under the belief that positive behavior can be taught and reinforced.
Let’s delve deeper into these core principles to understand how they shape the PBIS framework.
Prevention Over Punishment
One of the fundamental tenets of PBIS is the emphasis on proactive strategies to prevent behavioral issues rather than relying on punitive actions. The PBIS framework asserts that solely using punitive measures does not teach students the necessary skills for improving behavior. Instead, PBIS focuses on creating a positive school climate by setting clear behavior expectations and providing behavior support to prevent unwanted behaviors.
By prioritizing primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention, PBIS aims to address behavior challenges before they escalate, thereby improving outcomes for all students. This approach not only fosters good behavior but also enhances school safety and reduces reliance on exclusionary discipline practices.
Teaching Expected Behaviors
For PBIS to be effective, students must clearly understand what is expected of them. This involves instructing students about expected behaviors to ensure clarity and understanding. For students to meet behavior standards, they must be explicitly informed about what those standards entail. This clarity is achieved through the consistent communication of behavior expectations across all students, educators, and school staff.
Students need repeated practice to internalize new positive behaviors. Teaching clear behavior expectations and providing consistent practice opportunities help students learn and exhibit appropriate behaviors, thereby preventing unwanted behaviors and addressing problem behavior, enhancing the overall learning environment.
Consistent Implementation
Consistent application of PBIS strategies is crucial for creating a positive school climate and effective student behavior management. When PBIS is implemented consistently, it creates a shared expectation among students and staff, enhancing the effectiveness of behavior support. Every member of the school staff, from teachers to administrators, plays a crucial role in the consistent enforcement of PBIS strategies.
Collaboration and communication among all staff members ensure that students receive a unified message regarding expected behaviors. Ultimately, consistent implementation of PBIS enhances student engagement, behavior, and academic success, leading to durable improvements in school climate and student outcomes.
The Three-Tiered Support System
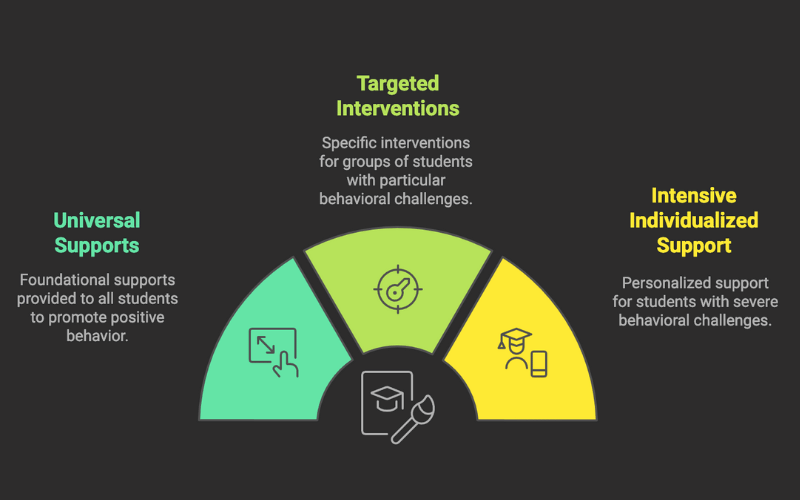
The PBIS framework consists of three tiers of increasingly intensive interventions designed to address different levels of student needs and provide appropriate support. This three-tiered system ensures that all students, regardless of their behavioral challenges, receive the support they need to succeed.
Students can receive support from multiple tiers of PBIS at the same time to effectively address their behavioral needs. Each tier contributes to the overall effectiveness of PBIS in unique ways.
Tier 1: Universal Supports
Tier 1 supports are foundational and provided to all students, including those with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and 504 plans. These universal supports focus on teaching students positive behavior strategies that are essential for their success in school. A behavior matrix outlines the positive behaviors expected from students, ensuring that they are familiar with these expectations as part of the PBIS framework.
As Tier 1 supports are implemented, negative behaviors in schools begin to diminish, leading to an increase in instructional time and overall student engagement. Approximately 80% of students typically remain at Tier 1 for interventions, highlighting its effectiveness in promoting a positive school climate and reducing the need for more intensive support.
Tier 2: Targeted Interventions
Tier 2 supports are designed for specific student groups and target their particular behavioral challenges. These targeted interventions provide additional support to students who do not respond adequately to Tier 1 strategies.
By focusing on secondary prevention, Tier 2 interventions aim to improve outcomes for approximately 15% of students who require more support than what is offered universally.
Tier 3: Intensive Individualized Support
Tier 3 focuses on providing personalized support for students exhibiting severe behavioral challenges. These intensive interventions are tailored to the unique needs of individual students who do not respond adequately to Tier 1 and Tier 2 supports.
By offering tertiary prevention, Tier 3 ensures that even the most challenging behaviors are addressed effectively, supporting students in achieving positive outcomes.
Key Elements of Successful PBIS Implementation
Successful PBIS implementation integrates evidence-based practices into the school environment to enhance student engagement and behavioral outcomes. Key elements include systems, practices, and anticipated outcomes, all of which contribute to a positive school climate.
Several essential components ensure the success of PBIS.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Utilizing data effectively allows PBIS teams to pinpoint specific questions they need to answer regarding the implementation and effectiveness of the framework. Data analysis provides insights that help schools refine their PBIS strategies, ultimately enhancing positive behaviors and academic outcomes. The Tiered Fidelity Inventory serves as a significant tool for schools to evaluate current PBIS practices, highlighting areas that need improvement.
Accumulated data supports informed adjustments to PBIS strategies, contributing to their overall effectiveness. Conducting a needs assessment is crucial in revealing deficiencies within current behavioral practices and pinpointing where improvements are necessary. Ensuring consistency in how negative behavior is handled is critical to the success of PBIS and contributes to maintaining a structured school environment.
Schoolwide Engagement
The success of PBIS depends on collaborative efforts from both teachers and administrators to create a unified philosophy on behavior management. A diverse PBIS team should involve representatives from administration, teachers, counseling, parents, and students. Active involvement of all members of the school community, including staff and families, is essential for the effective implementation of PBIS.
A strong PBIS team includes members from various roles within the school to ensure diverse perspectives. Stakeholders such as staff, parents, and students often need time to adjust to the changes brought by PBIS. Involvement of teachers, students, and families is crucial for a positive school climate.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Long-term positive changes from PBIS require persistent evaluation and adjustments over multiple school years. Regular assessment of PBIS initiatives is crucial to avoid ineffective practices that could waste resources. Implementing PBIS effectively necessitates a considerable commitment from educators and staff over time.
Monitoring implementation fidelity is essential for understanding how well the PBIS framework is executed in schools. Regular data review helps teams monitor the impact of their PBIS strategies and decide on necessary modifications. The approach of PBIS encourages constructive solutions rather than relying on disciplinary actions.

Implementing PBIS can significantly enhance the overall school climate, leading to increased student engagement and academic performance.
PBIS brings several specific benefits to school communities.
Enhanced School Climate
PBIS encourages the development of positive relationships between teachers and students, fostering a supportive learning environment. A positive school climate helps students develop essential social and emotional skills, contributing to their overall well-being. Research shows that PBIS leads to better student behavior, while traditional discipline practices are often ineffective at changing behavior and can be detrimental to academic achievement.
A positive school climate fosters student safety and respect, creating an environment where students feel valued and supported. This positive atmosphere enhances student outcomes and promotes a culture of respect and inclusion.
Improved Student Outcomes
Research shows that PBIS correlates with better academic achievements and social-emotional outcomes. A positive school climate leads to higher attendance, better academic achievement, and improved graduation rates. By focusing on teaching expected behaviors and providing consistent support, PBIS helps students succeed both academically and socially.
The PBIS framework also supports students with disabilities, aligning with the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to provide individualized supports and enhance student outcomes. This holistic approach ensures that all students, regardless of their needs, receive the support necessary to thrive in the school environment.
Reduction in Exclusionary Discipline Practices
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) framework aims at promoting positive behavior and decreasing the need for exclusionary practices such as suspensions and expulsions. PBIS shifts the focus from punitive measures to proactive, preventative strategies, helping to maintain a more conducive learning environment and reducing the incidence of behaviors that lead to suspensions.
Implementing PBIS leads to fewer suspensions and expulsions, creating an inclusive school environment that supports all students. The adoption of PBIS significantly contributes to a school’s overall climate, promoting safety and engagement among students.
Common Misconceptions About PBIS
Despite its numerous benefits, there are common misconceptions about PBIS that need to be addressed. Many believe PBIS is a simple solution to behavior issues, but in reality, it requires extensive time and effort for successful implementation.
Several misconceptions need clarification.
PBIS is Not a Quick Fix
One common misconception is that PBIS is a quick fix for behavior issues. However, implementing PBIS is a long-term commitment that requires changes in school culture and practices. Students may be wary of the transition to PBIS and the changes it entails. Parents might also feel that the implementation of PBIS results in a more lenient approach by the school.
Successful PBIS implementation necessitates systemic change and ongoing support from all stakeholders. It involves continuous monitoring, data analysis, and adjustments to strategies, ensuring that the framework evolves to meet the needs of the students and the school community.
PBIS Does Not Ignore Negative Behavior
Another misconception is that PBIS ignores negative behavior. In reality, PBIS incorporates logical consequences for misbehavior while prioritizing the encouragement of positive behavior. The framework aims to address negative behaviors through systematic interventions rather than overlooking them.
By integrating both proactive and reactive strategies, PBIS ensures that negative behaviors are addressed constructively. This balanced approach helps in maintaining a positive school climate and supports students in learning appropriate behaviors.
Steps to Implement PBIS in Your School
Implementing PBIS in a school involves several critical steps, from building a dedicated team to conducting a needs assessment and developing clear behavior expectations. These steps ensure a comprehensive and effective implementation of the PBIS framework, fostering a positive school climate and improving student outcomes.
Building a PBIS Team
The first step in implementing PBIS is forming a dedicated PBIS team. The team should consist of administrators, counselors, and classroom teachers. Additionally, families, caregivers, and students should also be included. Key roles within the team include a facilitator, an administrator for budget oversight, and a data specialist for tracking progress.
Building a PBIS team requires a long-term commitment and ongoing training to ensure sustainability and effectiveness. This team leads the efforts in promoting a positive school environment and ensures that PBIS strategies are implemented consistently across the school.
Conducting a Needs Assessment
Conducting a needs assessment is essential for identifying specific needs and assessing the effectiveness of current PBIS practices. Collecting and analyzing data provides insights into the success of behavior support initiatives and informs necessary adjustments to PBIS strategies.
Adjusting strategies based on findings ensures that the support provided is effective and responsive to student needs.
Developing and Teaching Behavior Expectations
Developing clear behavior expectations is crucial for student understanding and consistency in behavior management. Schools should ideally develop three to five specific behavior expectations to maintain clarity and focus.
Once these expectations are established, they must be taught consistently to all students. This involves creating opportunities for students to practice these behaviors repeatedly, ensuring that they internalize and exhibit expected behavior and appropriate behavior.
By teaching clear behavior expectations and providing regular reinforcement, schools can effectively manage student behavior and foster a positive learning environment.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of PBIS
Evaluating the effectiveness of PBIS is crucial for ensuring that the framework delivers the anticipated results and supports continuous improvement. This involves collecting and analyzing data, as well as making necessary adjustments to strategies based on findings.
Collecting and Analyzing Data
The PBIS Self-Assessment Survey (SAS) evaluates the effectiveness of behavior support systems in schools. Essential to assess PBIS implementation is determining whether the framework is delivering the anticipated results. Schools can assess office discipline referrals, teacher commitment, attendance, and academic achievement to evaluate the effectiveness of their PBIS framework.
Collecting and analyzing data enables schools to identify behavioral trends and tailor interventions to individual student needs. This data-driven approach ensures that PBIS strategies are refined and adapted to meet the evolving needs of the school community.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Findings
Evaluating accumulated data is crucial in determining the effectiveness of PBIS. The results gathered from evaluating PBIS allow schools to assess how well the practices are working. This iterative process ensures that PBIS practices evolve based on data and feedback to better support student behavior.
Ongoing evaluation allows schools to make timely adjustments to their PBIS practices before behavioral issues become entrenched. Continuously refining strategies based on data findings helps schools maintain a positive climate and enhance student outcomes.
Wrapping Up PBIS In Education
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a comprehensive framework designed to improve student behavior, enhance academic achievement, and create a positive school climate. By emphasizing proactive strategies, teaching expected behaviors, and ensuring consistent implementation, PBIS effectively addresses behavior challenges and supports student success.
Implementing PBIS requires a long-term commitment and collaboration among all stakeholders, including school staff, students, and families. Through continuous monitoring and improvement, schools can refine their PBIS strategies to better meet the needs of their students. By fostering a supportive and positive learning environment, PBIS helps schools achieve better student outcomes and a more inclusive school climate.
What is PBIS?
PBIS, or Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a structured framework designed to improve students’ behavioral, academic, and emotional outcomes by fostering a positive school environment and teaching appropriate behaviors. This approach emphasizes evidence-based practices to promote overall student well-being.
How does PBIS differ from traditional disciplinary methods?
PBIS differs from traditional disciplinary methods by focusing on teaching positive behaviors and preventing issues rather than punishing misbehavior. This proactive approach fosters a more supportive environment for students.
What are the three tiers of PBIS?
The three tiers of PBIS are Tier 1 (Universal Supports), Tier 2 (Targeted Interventions), and Tier 3 (Intensive Individualized Support), each designed to address varying levels of student needs effectively. This structured approach ensures that all students receive appropriate support based on their individual requirements.
How does PBIS benefit students?
PBIS significantly enhances students’ behavior and academic performance while promoting social-emotional learning. By cultivating a positive school environment, it encourages engagement and minimizes the use of exclusionary discipline.
What is required for successful PBIS implementation?
Successful PBIS implementation hinges on a dedicated team, data-driven decision making, and active involvement from the entire school community. Continuous monitoring and a commitment to improvement are essential for fostering a positive school environment.



