Classroom observation is a critical tool in the educational process, offering insights into teaching effectiveness, student engagement, and classroom dynamics. This article delves into various aspects of classroom observation, highlighting its importance and how it can be leveraged to improve teaching outcomes.
What is Classroom Observation?

Classroom observation refers to the practice of watching teachers and students during instructional time to gather data about teaching practices. This technique allows observers to assess how well educational objectives are being met and identify areas that may need improvement.
The observers can include peers, administrators, or external evaluators who sit in on classes, taking notes on instructional methods, classroom management, and student responses. The aim is to create a comprehensive understanding of the learning environment without disrupting the teaching process.
Classroom observation can take many forms, including structured observations, where specific criteria are used to evaluate teaching effectiveness, and unstructured observations, which are more open-ended and focus on the overall classroom dynamics. These different methodologies are part of the various approaches to classroom observations, allowing for both standardized and customized methods. This flexibility allows for a tailored approach that can address the unique needs of different educational settings. Additionally, observers may use various tools, such as checklists or rubrics, to systematically record their findings, ensuring that the data collected is both reliable and valid.
Furthermore, the feedback generated from classroom observations can be invaluable for professional development. Teachers can reflect on their practice based on the insights provided, leading to targeted improvements in their instructional strategies. This process not only enhances individual teaching effectiveness but also contributes to a culture of continuous learning within the school. As schools increasingly recognize the importance of collaborative growth, classroom observation serves as a vital mechanism for fostering a supportive environment where educators can share best practices and learn from one another.
The primary purpose of classroom observation is to enhance teaching and learning processes. By observing how classes are conducted, stakeholders can pinpoint strengths and weaknesses in pedagogical approaches. This systematic examination allows for a deeper understanding of the dynamics within the classroom, highlighting the components of effective classroom observation that contribute to an effective teaching and learning environment. Offering insights into how various teaching methods resonate with different student populations.
Classroom Observation Objectives Include:
- Identifying effective teaching strategies that promote student learning.
- Assessing student behavior and engagement during lessons.
- Providing targeted feedback to teachers for professional development.
- Informing curriculum design and instructional practices across the institution.
In addition to these objectives, classroom observation also serves as a vital tool for fostering collaboration among educators. By sharing observations and insights, teachers can learn from one another, creating a community of practice that encourages innovation and experimentation in teaching methods. This collaborative approach not only benefits individual educators but also contributes to a more cohesive educational environment where best practices can be disseminated and adopted widely.
Classroom observations can help in identifying the diverse needs of students, including those who may require additional support or alternative learning strategies. By closely monitoring student interactions and responses, observers can gather valuable data that informs differentiated instruction, ensuring that all learners have equitable access to educational opportunities. This focus on inclusivity is essential in today’s diverse classrooms, where understanding and addressing individual learning needs can significantly impact overall student success.
Conducting a Classroom Observation
To conduct a classroom observation effectively, pre-planning is essential. Observers must define the focus or objectives of the observation. This helps in analyzing relevant data post-observation effectively. Understanding the specific goals not only streamlines the observation process but also ensures that the observer is attuned to the nuances of the classroom environment.
Classroom Observation Steps To Consider:
- Set specific objectives for what needs to be observed.
- Inform the teacher about the observation’s purpose and parameters.
- Follow a structured format, utilizing observation forms to record findings.
- Engage in reflective practice post-observation to debrief and analyze gathered data.
Involving teachers in the observation process enhances their sense of ownership and allows for a more collaborative and supportive atmosphere. This collaborative approach not only fosters trust but also encourages teachers to share their insights and reflections, creating a rich dialogue about teaching practices and student engagement.
Moreover, it is beneficial to consider the diverse learning styles and needs of students during the observation. Observers should pay attention to how different instructional strategies impact student participation and understanding. By noting variations in student responses, observers can provide targeted feedback that addresses both strengths and areas for improvement. This comprehensive perspective can lead to more tailored professional development opportunities for educators, ultimately enhancing the overall learning experience in the classroom.
Effective Classroom Observational Techniques
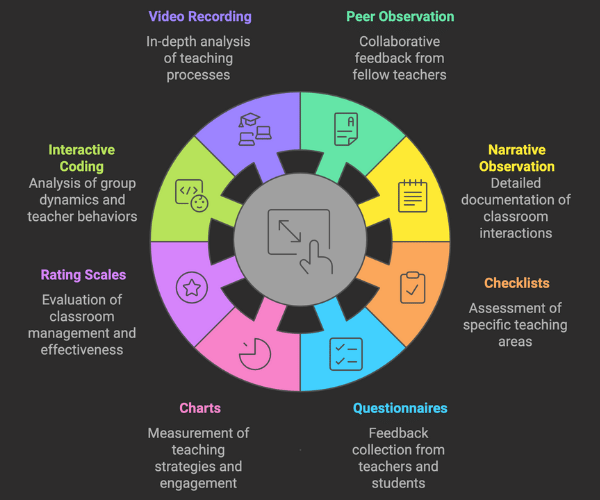
Various classroom observation techniques offer effective ways to evaluate teacher performance and refine teaching methodologies. Some of these techniques include:
- Peer Observation: Involves other teachers or a team observing and collaborating to provide valuable feedback, offering insights and suggestions for enhancement.
- Narrative Observation/Scripting: Entails taking detailed notes or using scripting techniques to document teacher actions, decisions, and interactions during the observation.
- Checklists: Used to assess specific areas such as lesson planning, assessments, and classroom management.
- Questionnaires and Surveys: Collect feedback from teachers and students regarding teaching practices, the classroom environment, and learning outcomes.
- Charts: Employed to record and measure teacher behavior, including teaching strategies and levels of student engagement.
- Rating Scales: Used to evaluate teachers on aspects like classroom behavior management, student engagement, and instructional effectiveness.
- Interactive Coding Systems: Observe and document group dynamics in relation to specific teacher behaviors, including classroom organization, instructional strategies, and student-teacher interactions.
- Video Recording: Allows for an in-depth analysis of teacher behavior, providing insights into the teaching process.
Using a combination of these techniques during classroom observations is crucial for gaining comprehensive insights into teacher performance and its impact on student learning.
In addition to these core techniques, it is essential to consider the context in which observations occur. For instance, the classroom environment, the diversity of student needs, and the specific learning objectives can all influence the effectiveness of observational strategies. By tailoring observational methods to fit the unique characteristics of each classroom, educators can gain a more nuanced understanding of student engagement and instructional effectiveness. Furthermore, incorporating feedback from students about their learning experiences can enrich the observational data, allowing teachers to adjust their approaches based on real-time insights.
The role of the observer is crucial in the process of classroom observation. Observers must remain objective and minimize their biases to ensure that their evaluations are valid and reliable. Training observers in reflective practices can enhance their ability to analyze interactions and teaching methods critically. Additionally, fostering a collaborative atmosphere where teachers feel comfortable receiving feedback can lead to more meaningful discussions about instructional practices and student outcomes. This collaborative approach not only benefits individual educators but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement within the school community.
Observations Strategies for Improved Teaching
Implementing effective observation strategies for improved effectiveness provides pathways for professional growth among educators. Strategies that can be employed include:
- Peer Observations: Facilitating teachers to observe one another fosters a supportive culture.
- Focused Walkthroughs: Administrators conducting brief, frequent observations to assess specific educational practices.
- Reflective Journals: Encouraging teachers to maintain journals that reflect on their teaching, informed by observational feedback.
Such strategies not only enhance the professional journey of teachers but also boost student engagement and achievement by focusing on time savings from streamlined observation processes that optimize instructional time.

Classroom observations offer numerous benefits for both teachers and students. For teachers, these observations provide invaluable feedback on their instructional practices, helping them identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement. This feedback can be used to refine teaching methods, leading to enhanced student learning outcomes. Additionally, classroom observations can help teachers develop their skills and confidence, ultimately boosting their overall performance.
For students, the benefits of classroom observations are equally significant. By identifying effective instructional strategies, teachers can create a more engaging and supportive learning environment. This, in turn, can lead to increased student motivation, participation, and academic achievement. Furthermore, observations can help teachers address any inequities in instruction, ensuring that all students have equal access to quality education. This focus on inclusivity is crucial in today’s diverse classrooms, where understanding and addressing individual learning needs can significantly impact overall student success.
Teacher Perspectives on Classroom Observations
Teachers may have varying perspectives on classroom observations, ranging from apprehension to appreciation. Some teachers may feel anxious or stressed about being observed, fearing that their teaching methods will be criticized or judged. However, many teachers recognize the value of observations in improving their practice and are open to constructive feedback.
Research suggests that teachers who receive regular feedback and coaching through observations are more likely to improve their instructional practices and student outcomes. Moreover, teachers who are involved in the observation process, such as through peer observation or self-reflection, are more likely to take ownership of their professional development and make meaningful changes to their teaching practices. This collaborative approach not only benefits individual educators but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement within the school community.
Observer Roles and Responsibilities
Observers play a crucial role in the classroom observation process. Their primary responsibility is to provide accurate and unbiased feedback on the teacher’s instructional practices. To achieve this, observers must be trained in effective observation techniques, such as using standardized rubrics and avoiding bias.
Observers should also be aware of their own roles and responsibilities, including:
- Providing clear and constructive feedback to the teacher.
- Maintaining confidentiality and respect for the teacher’s privacy.
- Avoiding judgment or criticism, focusing instead on specific behaviors and practices.
- Observers should also be aware of their own roles and responsibilities, including using technology, such as video recording or digital tools like classroom observation apps, to enhance the observation process.
- Engaging in ongoing professional development to improve their observation skills.
By fulfilling these roles and responsibilities, observers can help ensure that classroom observations are a valuable and supportive experience for teachers, ultimately leading to improved student learning outcomes. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the effectiveness of classroom observations but also fosters a culture of continuous learning and development within the educational community.
Overcoming Challenges in Classroom Observation
Challenges with traditional classroom observation are not without their challenges. Observers may face several obstacles, including potential biases, the fear of misinterpretation, and the anxiety some teachers feel during evaluations.
Strategies To Mitigate These Challenges Include:
- Training observers to recognize and minimize biases.
- Establishing a clear framework for observations that outlines expectations and procedures.
- Encouraging a growth mindset among teachers to view observations as opportunities rather than threats.
Addressing these challenges can improve the overall effectiveness of the classroom observation process.
Innovative Methods for Classroom Observation
Innovative methods for conducting classroom observation are rapidly evolving, harnessing technology to enable enhanced classroom observations. These advancements offer new ways to gather and analyze data, making observations more efficient and effective. Below, we explore several examples of these cutting-edge approaches.
Online Observation Tools
Online observation tools offer a digital platform for conducting classroom observations, allowing observers to enter data in real-time. These tools often come with features such as customizable checklists, automated data analysis, and the ability to generate reports instantly. By using online tools, observers can efficiently track teaching practices and student engagement without the cumbersome paperwork, making the observation process more streamlined and effective. These tools also facilitate easier sharing of observations with educators, enabling timely feedback and collaboration.
Mobile Applications
Mobile applications designed for classroom observation provide a convenient way for teachers and observers to gather and analyze feedback. These apps often include features such as voice-to-text capabilities, photo documentation, and timestamping, which help capture detailed observation data quickly. The portability of mobile devices means that observations can be conducted seamlessly without disrupting the classroom environment. Additionally, these apps can integrate with other educational software, providing a comprehensive view of teaching effectiveness and areas for improvement.
Virtual Reality (VR) Simulations
Virtual Reality (VR) simulations offer an innovative approach to classroom observation by creating immersive learning experiences for observers. Through VR, observers can experience a classroom setting virtually, allowing them to focus on specific teaching strategies and student interactions without being physically present. This technology can be particularly beneficial for training new observers or for conducting observations in diverse educational contexts. VR simulations can also be used to model various classroom scenarios, providing educators with insights into different instructional methods and their impact on student learning.
These innovations can help streamline the observation process, making it more efficient and effective for all stakeholders involved.
Feedback is a vital component of the classroom observation process. Constructive feedback focuses on teacher behavior, promoting professional growth and enhancing teaching practices.
Constructive Feedback Should Be:
- Specific: Focus on particular instances or practices observed.
- Actionable: Provide suggestions for improvement that can be easily implemented.
- Timely: Offer feedback shortly after the observation to ensure relevance.
Implementing a systematic feedback mechanism fosters a collaborative culture within the educational setting, where teachers feel supported and empowered.
3 Best Practices for Classroom Observation
To maximize the benefits of teacher observation and classroom observation, several best practices should be adhered to:
1. Foster a Collaborative Environment

Creating a collaborative environment is essential for effective classroom observation. This involves establishing a culture where observations are viewed not as evaluations but as opportunities for growth and learning. Encouraging open communication between observers and teachers helps build trust and reduces the anxiety often associated with being observed. By fostering a supportive atmosphere, teachers are more likely to embrace feedback and use it to enhance their instructional practices. Collaborative environments also promote the sharing of best practices among educators, leading to a more cohesive and innovative teaching community.
2. Ensure Constructive Feedback Sessions
Constructive feedback is a cornerstone of the observation process. Feedback sessions should be carefully structured to focus on specific, observable behaviors and practices, rather than personal attributes. Providing feedback that is respectful and focused helps teachers understand their strengths and areas for improvement. It is crucial to offer actionable suggestions that teachers can implement in their classrooms. By ensuring that feedback is delivered in a timely manner, teachers can make immediate adjustments to their teaching methods, leading to continuous professional development and improved student outcomes.
3. Encourage Self-Reflection Among Teachers

Self-reflection is a powerful tool for personal and professional growth. Encouraging teachers to engage in self-reflection as part of the observation process allows them to critically assess their teaching practices and identify areas for enhancement. Self-reflection empowers teachers to take ownership of their development, fostering a proactive approach to professional growth. Incorporating reflective practices, such as journaling or peer discussions, can deepen teachers’ understanding of their instructional strategies and their impact on student learning. This introspective approach not only benefits individual educators but also contributes to a culture of lifelong learning within the school community.
By integrating these best practices, educators can ensure that classroom observation serves as a meaningful and developmental tool.
The Future of Classroom Observations
The future of classroom observations looks promising as educational environments increasingly value data-driven decision-making. As technology advances, so will the methods and tools available for classroom observation.
We are likely to see a significant shift toward more personalized and adaptive observation practices, utilizing software for enhanced classroom observations. These can include customized observation frameworks tailored to individual teacher needs and innovative performance metrics that assess educator effectiveness.
Classroom Observations With Education Walkthrough
Education Walkthroughs software offers a cutting-edge solution for school leaders aiming to enhance educational outcomes through structured classroom observations. This software for enhanced classroom observations transforms traditional methods of teaching assessments, improving efficiency in data collection and providing comprehensive analytics. This platform provides a comprehensive model for collecting real-time observational data, enabling decision-makers to gain deeper insights into classroom dynamics and teaching practices.
The Benefits of Implementing Education Walkthroughs Software Include:
- Streamlined Data Collection: The software facilitates efficient observation of multiple classrooms over a designated period, allowing for the seamless gathering of valuable data without disrupting the learning environment.
- Engagement of Stakeholders: By involving various stakeholders, including teachers and administrators, the platform promotes a collaborative approach to understanding and improving educational practices.
- Informed Professional Development: Analysis of the collected data helps identify trends and areas for improvement, informing targeted professional development efforts that are tailored to the needs of educators.
School leaders should consider implementing Education Walkthroughs software to elevate classroom observation practices. By leveraging this innovative tool, schools can foster a culture of continuous improvement, enhance instructional practices, and ultimately improve student learning outcomes.



